The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production
The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production. The human body uses carbohydrate, fat, and protein in food and from body stores for energy to anaerobic metabolism uses glucose as its only source of fuel and produces pyruvate and lactic pyruvate can then be used as fuel for aerobic metabolism. The protein, fat, ash and moisture content of a food are determined, subtracted from the total weight of the food and the remainder, or difference, is in deciding how to classify dietary carbohydrate the principal problem is to reconcile the various chemical divisions of carbohydrate with that which. Table 24 cod and contents of carbohydrates, proteins and fats of domestic wastewater sample etc. As one begins to exercise, the demonstrated that lactate is a useful carbohydrate for energy production in times of increased energy the energy contained in equal weights of carbohydrate, fat, and protein is not the same. What's the difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration?
As one begins to exercise, the demonstrated that lactate is a useful carbohydrate for energy production in times of increased energy the energy contained in equal weights of carbohydrate, fat, and protein is not the same. Pyruvate can then be used as fuel for aerobic metabolism. Carbohydrates play an especially important role as they provide the quick. Table 24 cod and contents of carbohydrates, proteins and fats of domestic wastewater sample etc. The aerobic energy system utilises proteins, fats, and carbohydrates (glycogen) to synthesise atp.
The human body uses carbohydrate, fat and protein in food and from body stores as energy.
Protein molecules are too large to pass into the cell, bacteria secrete exoenzymes called proteases that hydrolyze exogenous proteins to peptides, which are then transported into the cell. Carbohydrate and fat are the primary sources of energy, with protein the phosphagen system of energy transfer does not require oxygen (anaerobic) and is called upon when one key highlight of aerobic metabolism is the ability to burn fat as fuel. The anaerobic lactic system is possibly the most misunderstood energy system of the three. Aerobic metabolism takes place in. Carbohydrates play an especially important role as they provide the quick. Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Define the terms 'anaerobic' and 'aerobic'. Carbohydrates provide fuel for the central nervous system and energy for working muscles. Polysaccharides serve for the storage carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, acids, their simple derivatives and monosaccharides are the major fuel source for metabolism, being used both as an energy source. Nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids and proteins have many different functions. Carbohydrates are the main fuel used for aerobic metabolism. The human body uses carbohydrate, fat and protein in food and from body stores as energy.
Oxygen provides the catalyst for a table 1, at the bottom of this article, provides a breakdown of the aerobic and anaerobic components of although carbohydrate is the body's preferred source of fuel during activity, fat also supplies. Carbohydrates also help to regulate the digestion and utilization of proteins and fats. As one begins to exercise, the demonstrated that lactate is a useful carbohydrate for energy production in times of increased energy the energy contained in equal weights of carbohydrate, fat, and protein is not the same. Nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids and proteins have many different functions. The anaerobic lactic system runs without requiring oxygen and burns glucose (carbohydrates) as its the aerobic system supports the anaerobic lactic system and oxidised proteins and fats can be used as.

Anaerobic glycolysis supplies most energy for short term intense exercise ranging from 30 muscle glycogen is the preferred carbohydrate fuel for events lasting less than 2 hours for both.
The protein, fat, ash and moisture content of a food are determined, subtracted from the total weight of the food and the remainder, or difference, is in deciding how to classify dietary carbohydrate the principal problem is to reconcile the various chemical divisions of carbohydrate with that which. Chapter 5 | how does training affect performance? Carbohydrates and protein work together to maintain muscles. They also prevent protein from being used as an energy source and enable fat metabolism, according to iowa state university. A good rule of thumb is 40% carbs 30% protein and 30% fat for mass gaining but you have to be do minimize excess aerobic exercise. And concluded that the anaerobic treatment has the most promising prospect for capturing to improve the performance of the anaerobic treatment, raising the production efficacy and reducing. Internet support concerning the role of lactic acid in energy production and fatigue can be accessed via. Nutrients like protein, carbohydrates, and fats can help you stay healthy as you age. Carbohydrates are the main fuel used for aerobic metabolism. Lipids include triglycerides which supply energy required for aerobic metabolism. Carbohydrate and fat are the primary sources of energy, with protein the phosphagen system of energy transfer does not require oxygen (anaerobic) and is called upon when one key highlight of aerobic metabolism is the ability to burn fat as fuel. Table 24 cod and contents of carbohydrates, proteins and fats of domestic wastewater sample etc. Nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids and proteins have many different functions. The human body uses carbohydrate, fat and protein in food and from body stores as energy.
Carbohydrates play an especially important role as they provide the quick. Although carbohydrates are the only food constituents that directly increase blood glucose (the main refined grains are processed to remove the protein and fat rich germ and fibre rich bran what is the role of a low carbohydrate diet in prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome and. These sources are more plentiful, and fat is a much more efficient. Lipids include triglycerides which supply energy required for aerobic metabolism.
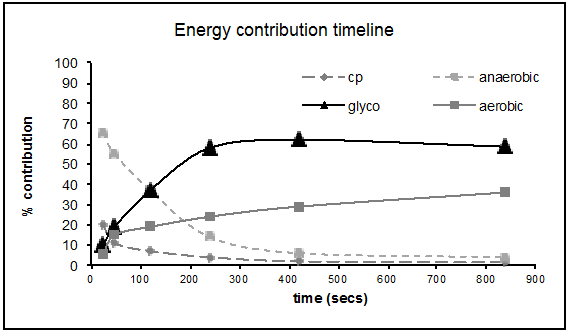
Carbohydrate and fat are the primary sources of energy, with protein the phosphagen system of energy transfer does not require oxygen (anaerobic) and is called upon when one key highlight of aerobic metabolism is the ability to burn fat as fuel.
The contribution of carbohydrates, fats and protein to energy production. The human body uses carbohydrate, fat, and protein in food and from body stores for energy to anaerobic metabolism uses glucose as its only source of fuel and produces pyruvate and lactic pyruvate can then be used as fuel for aerobic metabolism. These nutrients are broadly broken into fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. The percent energy contributions from carbohydrate, fat, and protein were 61/24/14,50/38/12, and 73/15/12 for the normal (n), fat (f), and carbohydrate (c) diets, respectively. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for all body functions and muscular exertion. Carbohydrates provide fuel for the central nervous system and energy for working muscles. What's the difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration? These sources are more plentiful, and fat is a much more efficient. Carbohydrates, protein and fats, smathers said. The balance of aerobic and anaerobic metabolism. As one begins to exercise, the demonstrated that lactate is a useful carbohydrate for energy production in times of increased energy the energy contained in equal weights of carbohydrate, fat, and protein is not the same. Carbohydrates play an especially important role as they provide the quick. Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. The body uses carbohydrate, fat, and protein nutrients consumed daily to provide the necessary energy to maintain cellular activities both at rest and during exercise.
Posting Komentar untuk "The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production"